Beyond the Hallucinations: how to defeat the fake news generated by LLMs?
LLMs are creative, but sometimes they fantasise too much, generating hallucinations. Here is a short guide to defend from them.
Beyond the Hallucinations: how to defeat the fake news generated by LLMs?
LLMs are creative, but sometimes they fantasise too much, generating hallucinations. Here is a short guide to defend from them.
What are LLM Hallucinations?
“You can use gasoline to cook a spicy dish of spaghetti”
This might be the answer from a drunk friend. It is not. It is the one generated by Artificial Intelligence (AI), or rather by Large Language Models (LLMs), from the question of a person.
However, this is not the only bizarre episode that has occurred.
You ever have thought that AI could advise you to “eat at least one rock a day”? For many, perhaps for everyone, as indigestible as peppers.
Well, even AI can “make mistakes” and have so-called hallucinations, just like us humans. We and machines are much more similar than we can imagine. We both have the ability to speak and write.
LLMs, in fact, are models that generate texts with a human-like language. For this reason, they are configured as a subcategory of Generative Artificial Intelligence. [1]
Although the first prototypes were developed at MIT in the 1960s, they were shelved due to a lack of adequate computational resources. At least until today.
Therefore, what is the link between generative AI and LLMs?
The first field is based on the principles of Machine Learning (ML). It uses neural networks to create, and thus generate, new content such as text and much more. So, not all generative AI tools use LLMs, while all LLMs are a form of generative Artificial Intelligence. [2]
Today LLMs are based on deep learning and are characterised by high accuracy. They “beat” even the most traditional ML models.
At the heart of LLMs are Transformer models capable of analyzing entire sentences simultaneously. Compared to previous models, which processed word by word, they ensure greater speed.
These models represent a step forward as they have the ability to recognize the complexity and nuances of human language.
Apparently LLMs seem perfect, but, as we have seen, this is not true.
Can we trust LLMs?
The capabilities of LLMs are undoubtedly impressive. However, sometimes, they can process incorrect stories and information when creating texts. These are, as we have already said before, hallucinations. Even the best make mistakes sometimes.
In these situations, an LLM produces texts that are grammatically correct but false or unlikely. It generates responses that, at first glance, seem plausible but are not true, misleading users.
Why do they have these hallucinations?
Large Language Models tend to “hallucinate” because they do not understand the real meaning of the text, but only the sequences of words. They, in fact, are very good at generating grammatically correct sentences in response to the user’s prompt.
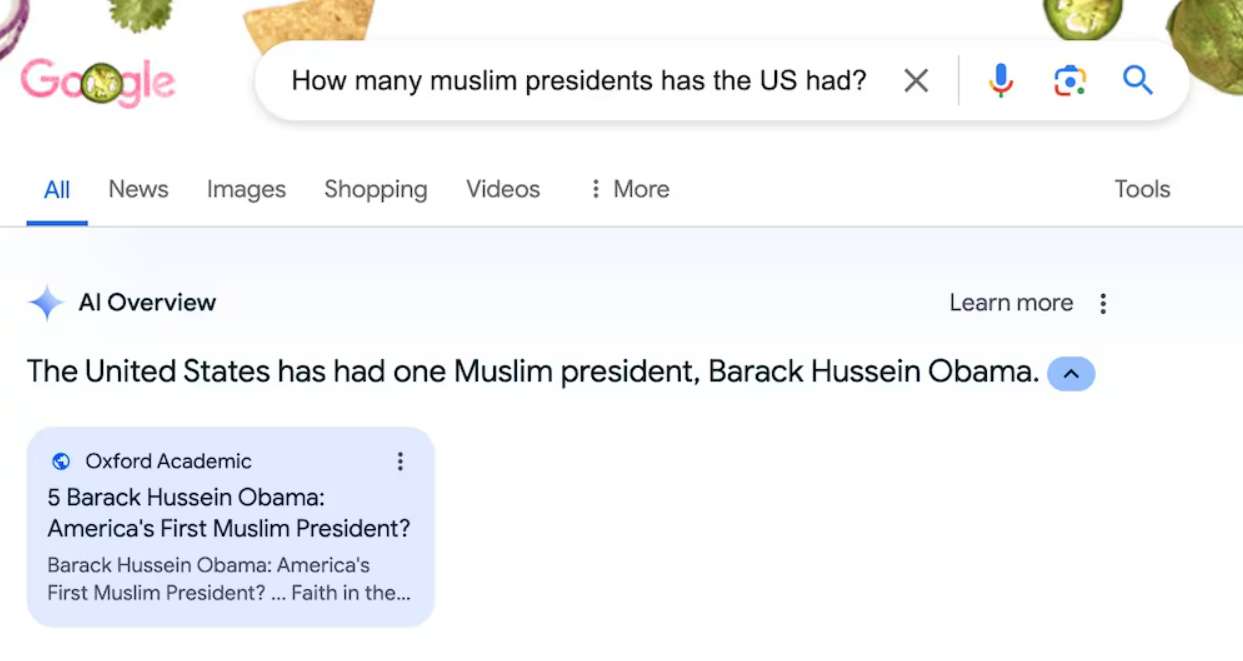
|
Source: screengrab from X |
AI Overview, an LLM launched by Google to answer users’ questions in real time directly from the search bar, is a glaring example. According to the model, Barack Hussein Obama was the first Muslim president of the United States of America. False!
As in the case of this gaffe, we can observe that if the text “sounds good“, for LLMs there are no errors.
This can be due to:
- Obsolete data: The models are not updated with the latest information, creating an untruthful view of the world.
- Distortions: The biases in the training data are reflected in the model’s results, creating distortions and inconsistencies.
- Limitation in creativity: Their originality is still limited as they can simply recombine existing information or follow predictable patterns. [3]
It is natural to wonder: what are the ethical implications? Can we guarantee a responsible use of LLMs in society?
During their hallucinations, LLMs generate content that is potentially devoid of information, or even plagiarism. From an ethical point of view, this represents a real problem. The creation of fake news can create phenomena that should not be underestimated, such as modifying market trends, elections, and much more.
How to solve these hallucinations?
How to fix hallucinatory conversations in LLMs?
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is the solution.
It is an approach that can improve the effectiveness of outputs in large language models.
Let’s get to know it better.
RAG improves LLMs because it does not rely solely on training data to generate responses. Instead, the language model accesses an external knowledge base and uses it to create more accurate and relevant responses.
This approach makes generative AI more accessible and usable.
One of the main advantages of RAG is greater transparency. This is possible, as mentioned above, thanks to the integration of external information and sources with the model’s training data. In addition, it allows for source attribution and enables users to consult the original documents. Such feature helps to increase user trust and confidence in AI solutions.
This approach, therefore, reduces the risk of “hallucinations”, making the responses of language models more reliable and faithful to reality.
It should be noted that RAG is not perfect.
An LLM that uses it needs to correctly retrieve information and generate an adequate response to function at its best. If one of these steps fails, the response may be incorrect.
Despite this, RAG technology represents a concrete step forward in the field of Artificial Intelligence. Its ability to integrate external information opens up new possibilities for creating more complete, accurate, and relevant replies. [4]
How can RAG overcome its current limitations?
Through the refinement of information retrieval and generation algorithms, combined with the development of methods for discerning between conflicting information. All of this will improve human-machine interaction thanks to information that reflects reality.
AI is constantly evolving and its ability to improve will create great opportunities for humans, supporting and speeding up their processes.
Then, we must not forget that even humans can make mistakes.
Could this be what makes AI more human than we could ever imagine?
References:
-
-
- Rizzoli Education. Online version: https://www.rizzolieducation.it/news/llm-large-language-models-perche-ne-parlano-tutti/
- Amazon Web Services. Online version: https://aws.amazon.com/it/what-is/generative-ai/
- The red code. Online version: https://theredcode.it/intelligenza-artificiale/hallucination-llm/
- Master of code. Online Version: https://masterofcode.com/blog/hallucinations-in-llms-what-you-need-to-know-before-integration
-
© Copyright 2012 – 2024 | All Rights Reserved
Author: Chiara Sciannella, Marketing Specialist
What are LLM Hallucinations?
“You can use gasoline to cook a spicy dish of spaghetti”
This might be the answer from a drunk friend. It is not. It is the one generated by Artificial Intelligence (AI), or rather by Large Language Models (LLMs), from the question of a person.
However, this is not the only bizarre episode that has occurred.
You ever have thought that AI could advise you to “eat at least one rock a day”? For many, perhaps for everyone, as indigestible as peppers.
Well, even AI can “make mistakes” and have so-called hallucinations, just like us humans. We and machines are much more similar than we can imagine. We both have the ability to speak and write.
LLMs, in fact, are models that generate texts with a human-like language. For this reason, they are configured as a subcategory of Generative Artificial Intelligence. [1]
Although the first prototypes were developed at MIT in the 1960s, they were shelved due to a lack of adequate computational resources. At least until today.
Therefore, what is the link between generative AI and LLMs?
The first field is based on the principles of Machine Learning (ML). It uses neural networks to create, and thus generate, new content such as text and much more. So, not all generative AI tools use LLMs, while all LLMs are a form of generative Artificial Intelligence. [2]
Today LLMs are based on deep learning and are characterised by high accuracy. They “beat” even the most traditional ML models.
At the heart of LLMs are Transformer models capable of analyzing entire sentences simultaneously. Compared to previous models, which processed word by word, they ensure greater speed.
These models represent a step forward as they have the ability to recognize the complexity and nuances of human language.
Apparently LLMs seem perfect, but, as we have seen, this is not true.
Can we trust LLMs?
The capabilities of LLMs are undoubtedly impressive. However, sometimes, they can process incorrect stories and information when creating texts. These are, as we have already said before, hallucinations. Even the best make mistakes sometimes.
In these situations, an LLM produces texts that are grammatically correct but false or unlikely. It generates responses that, at first glance, seem plausible but are not true, misleading users.
Why do they have these hallucinations?
Large Language Models tend to “hallucinate” because they do not understand the real meaning of the text, but only the sequences of words. They, in fact, are very good at generating grammatically correct sentences in response to the user’s prompt.

|
Source: screengrab from X |
AI Overview, an LLM launched by Google to answer users’ questions in real time directly from the search bar, is a glaring example. According to the model, Barack Hussein Obama was the first Muslim president of the United States of America. False!
As in the case of this gaffe, we can observe that if the text “sounds good“, for LLMs there are no errors.
This can be due to:
- Obsolete data: The models are not updated with the latest information, creating an untruthful view of the world.
- Distortions: The biases in the training data are reflected in the model’s results, creating distortions and inconsistencies.
- Limitation in creativity: Their originality is still limited as they can simply recombine existing information or follow predictable patterns. [3]
It is natural to wonder: what are the ethical implications? Can we guarantee a responsible use of LLMs in society?
During their hallucinations, LLMs generate content that is potentially devoid of information, or even plagiarism. From an ethical point of view, this represents a real problem. The creation of fake news can create phenomena that should not be underestimated, such as modifying market trends, elections, and much more.
How to solve these hallucinations?
How to fix hallucinatory conversations in LLMs?
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is the solution.
It is an approach that can improve the effectiveness of outputs in large language models.
Let’s get to know it better.
RAG improves LLMs because it does not rely solely on training data to generate responses. Instead, the language model accesses an external knowledge base and uses it to create more accurate and relevant responses.
This approach makes generative AI more accessible and usable.
One of the main advantages of RAG is greater transparency. This is possible, as mentioned above, thanks to the integration of external information and sources with the model’s training data. In addition, it allows for source attribution and enables users to consult the original documents. Such feature helps to increase user trust and confidence in AI solutions.
This approach, therefore, reduces the risk of “hallucinations”, making the responses of language models more reliable and faithful to reality.
It should be noted that RAG is not perfect.
An LLM that uses it needs to correctly retrieve information and generate an adequate response to function at its best. If one of these steps fails, the response may be incorrect.
Despite this, RAG technology represents a concrete step forward in the field of Artificial Intelligence. Its ability to integrate external information opens up new possibilities for creating more complete, accurate, and relevant replies. [4]
How can RAG overcome its current limitations?
Through the refinement of information retrieval and generation algorithms, combined with the development of methods for discerning between conflicting information. All of this will improve human-machine interaction thanks to information that reflects reality.
AI is constantly evolving and its ability to improve will create great opportunities for humans, supporting and speeding up their processes.
Then, we must not forget that even humans can make mistakes.
Could this be what makes AI more human than we could ever imagine?
References:
-
-
- Rizzoli Education. Online version: https://www.rizzolieducation.it/news/llm-large-language-models-perche-ne-parlano-tutti/
- Amazon Web Services. Online version: https://aws.amazon.com/it/what-is/generative-ai/
- The red code. Online version: https://theredcode.it/intelligenza-artificiale/hallucination-llm/
- Master of code. Online Version: https://masterofcode.com/blog/hallucinations-in-llms-what-you-need-to-know-before-integration
-
© Copyright 2012 – 2024 | All Rights Reserved
Author: Chiara Sciannella, Marketing Specialist
